Page 90 - Giáo trình môn học Cấu tạo cơ thể
P. 90
O O O
NH 2
AMP H H H
N deaminase N N N N
N N N
N N H 2 O NH 4 + N N O N N H 2 N N N
Rib P Rib P H Rib P H Rib P
AMP IMP XMP GMP
H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O H 2 O
nucleotidase nucleotidase nucleotidase nucleotidase
Pi adenosin Pi Pi Pi
deaminase
Adenosin Inosin Xanthosin Guanosin
H 2 O NH 4 + Pi purine Pi purine P i purine
nucleoside nucleoside nucleoside
Ribose -1-P phosphorylase Ribose -1-P phosphorylase Ribose -1-P phosphorylase
(PNP) (PNP) (PNP)
xanthine guanine
oxidase deaminase
Hypoxanthin Xanthin Guanin
O 2 + H 2 O H 2 O 2 NH 4 + H 2 O
O 2 + H 2 O xanthine
oxidase
H 2 O 2
O
H
H N
N
O
O N N
H
H
Acid uric
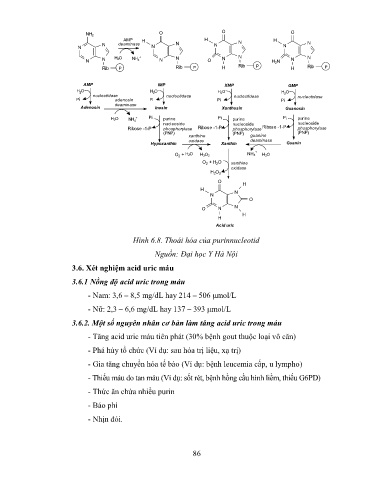
Hình 6.8. Thoái hóa của purinnucleotid
Nguồn: Đại học Y Hà Nội
3.6. Xét nghiệm acid uric máu
3.6.1 Nồng độ acid uric trong máu
- Nam: 3,6 – 8,5 mg/dL hay 214 – 506 μmol/L
- Nữ: 2,3 – 6,6 mg/dL hay 137 – 393 μmol/L
3.6.2. Một số nguyên nhân cơ bản làm tăng acid uric trong máu
- Tăng acid uric máu tiên phát (30% bệnh gout thuộc loại vô căn)
- Phá hủy tổ chức (Ví dụ: sau hóa trị liệu, xạ trị)
- Gia tăng chuyển hóa tế bào (Ví dụ: bệnh leucemia cấp, u lympho)
- Thiếu máu do tan máu (Ví dụ: sốt rét, bệnh hồng cầu hình liềm, thiếu G6PD)
- Thức ăn chứa nhiều purin
- Báo phì
- Nhịn đói.
86